What Is Bitcoin Private Key? Everything You Need To Know !!

Thinking of buying some Bitcoin & HODL-ing it? Great.
But let me tell you if your private key is not kept safe, you are doomed.
Let me be honest and admit that:
“Your Bitcoin is only as safe as the private keys”
Even the most popular Bitcoin evangelist-Andreas M. Antonopoulos, has said this several times:
“Your Keys, Your Bitcoin. Not Your Keys, Not Your Bitcoin”
But we still keep hearing about the new private key hacks every day, which shows that this concept of ‘Private Keys’ is still not well understood.
That’s why I will attempt to explain the concept of private keys related to Bitcoin and cryptocurrency in general and hope that it will help Bitcoiners adopt a more proactive approach to safeguarding their private digital keys.
So let’s begin:
Introduction: Bitcoin Private Keys
Private and public keys of Bitcoin are just a bunch of alphanumeric digits.
Anyone having this secret number can spend those Bitcoins, and that’s why a private key needs to be guarded very carefully.
Usually, this key resides in a Bitcoin wallet file and for those of you who aren’t familiar with a Bitcoin wallet file, here is a simplistic explanation.
A Bitcoin wallet is merely a combination of a private key and a public key.
So if you have this combination on a piece of paper, it is called a paper wallet, or if they are on a mobile device, it is called a mobile wallet.
To understand the concept of private keys, let me give you an example:
Imagine this:
You are Bob, who wants to send a letter to Alice. You both are friends.
Now to do this, Bob needs to know Alice’s postal address or postbox number. This post box number is public, and the index number is known to Alice and her friends & family, like Bob.
Moreover, Alice can always tell this post box number to anyone she wants to receive letters from.
Let’s assume the letter has been posted in the post box, but to actually receive the letter, Alice needs to use her post box keys to unlock the box and take out her letters.
This key is personal to Alice, and she safeguards it because she knows that anyone in possession of this same key can take her letters.
So, in this case, the post box number or address is actually the same public key or public address in the Bitcoin realm and the letterbox key is like the private key of your wallet.
Watch this to understand more about Bitcoin keys:
So, in short, a private key of Bitcoin is just a 256-bit number which can be denoted in several formats and is used to spend/send Bitcoins from one address to another.
But the most common type of private key format is shown below, and it usually starts with ‘5’:
Private key example: 5KVrxY3ZMQX8mWPXhLrZuvgKBMYLTiEgruhJZMbTGPEjdbQbFc7
There are many other types used for the same private key and we are going to discuss in the next section because these private key formats are integral to understanding private keys as a whole.
So stick with me…
Private Key Format Bitcoin
Here are some of the most popular private and public key formats of Bitcoin that are used in different types of wallets nowadays:
#1. Raw Private Key
A private key (in Bitcoin, i.e. ECDSA SECP256K1) is a 32-byte number between 0x1 and 0xFFFF FFFF FFFF FFFF FFFF FFFF FFFF FFFE BAAE DCE6 AF48 A03B BFD2 5E8C D036 4140.
For example 0C28FCA386C7A227600B2FE50B7CAE11EC86D3BF1FBE471BE89827E19D72AA1D
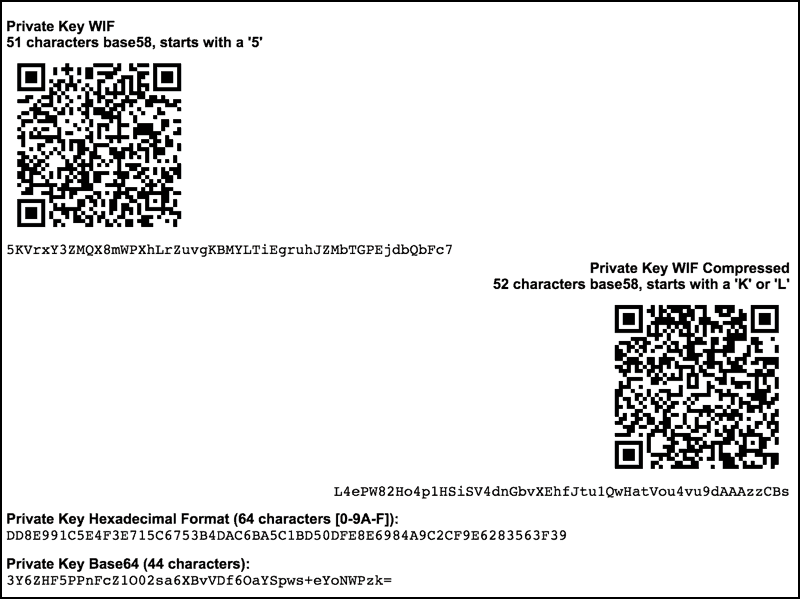
#2. Private Key WIF (WIF- Wallet Import Format)
This type of private key has 51 characters base58, starts with a ‘5’. It is also shorter and includes a checksum in case of typos.
For example: 5KVrxY3ZMQX8mWPXhLrZuvgKBMYLTiEgruhJZMbTGPEjdbQbFc7
#3. Private Key WIF Compressed (WIFC- Wallet Import Format Compressed)
This type of private key has 52 characters base58, starts with a ‘K’ or ‘L.’ For example: L4ePW82Ho4p1HSiSV4dnGbvXEhfJtu1QwHatVou4vu9dAAAzzCBs
#4. Private Key Hexadecimal Format (HEX)
This private key format has 64 characters [0-9A-F] and looks like this: DD8E991C5E4F3E715C6753B4DAC6BA5C1BD50DFE8E6984A9C2CF9E6283563F39
#5. Private Key (B64)
This private key format has Base64 (44 characters) and looks like this: 3Y6ZHF5PPnFcZ1O02sa6XBvVDf6OaYSpws+eYoNWPzk=
#6. Mini
This type of Bitcoin key format is used where space is very critical such as on QR code cards or on physical Bitcoin address cards. This can be a mini private key or public keys.
Mini keys look like this: SzavMBLoXU6kDrqtUVmffv
What Is A Bitcoin Public Key (or Address)?
A Bitcoin uncompressed public key is another alphanumeric number associated with Bitcoin on which coins are sent or received.
And the fun fact is, Bitcoin public keys (or address) are derived from private keys of Bitcoin only by applying mathematical operations over the private keys to form the corresponding public keys by using Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC)
Furthermore, these public keys can be transformed into Bitcoin public addresses, and each of the transformations from private key generation to the public key to public address is irreversible. The addresses generated from this method can be used as the address to people can be sent Bitcoin to.
And this irreversibility by maths has been the foundation of Bitcoin- the world’s first fully functional cryptocurrency.
This is how a transformed public key looks like and it usually will represent private keys that start with the digit ‘1’ and recently due to segwit addresses you will find public addresses or public keys starting with digit ‘3’ also.
Public key example: 1CuzgGMPNLuCd3AWpG53H2qnFaDANq1z5X
How Do Bitcoin Keys Work?
Bitcoin is essentially a messaging system based on public-key cryptography or better known as asymmetric cryptography, that uses two systems of keys for super-efficient encryption and communication.
Bitcoin uses public keys (or addresses) and private keys to encrypt and decrypt data (transactions value-Bitcoins).
The keys are simply large numbers that have been paired together but are not identical (asymmetric). They are called key pairs.
One key in the pair can be shared with everyone; it is called the public key.
The other key in the pair is kept secret; it is called the private key.
Either of the keys can be used to encrypt a message; the opposite key from the one used to encrypt the message is the master key used for decryption. (Source-techtarget.com)
See this to understand better:
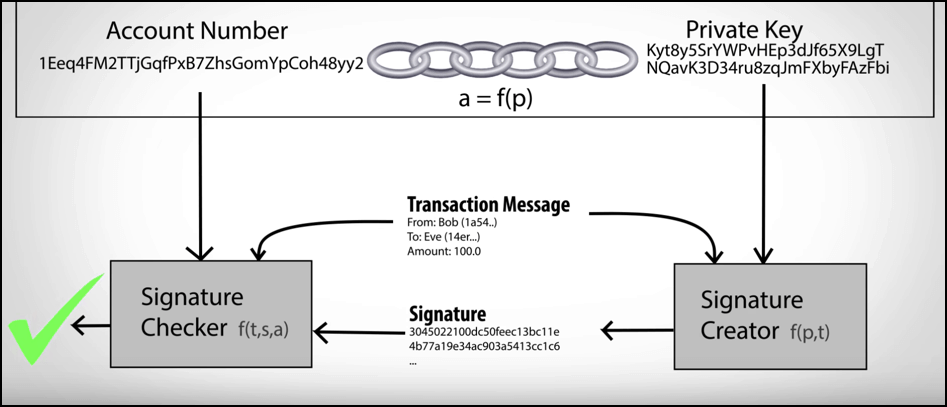
In Bitcoin, it is ensured that the sender is the real owner of the account from which they are sending, and this happens through signatures that are verified by this asymmetric algorithm or function.
And this ‘signature’ is a number that proves that the rightful owner of the key will sign transactions.
A signature is mathematically generated from the hashed form of a transaction message plus the private key and is an irreversible mathematical operation.
And further, anyone can feed the known public key and this signature in a special cryptographic function to determine that the signature was originally produced from the hash of the transaction message plus the same private key itself, without needing to know the private key.
This ensures that the sender/signer is the real owner of Bitcoins and that no malicious actors can gain access to the key pair.
How Is A Bitcoin Private Key Generated?
Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm or ECDSA is the asymmetric cryptographic algorithm used by Bitcoin to generate public and private keys.
And this asymmetric nature ensures that only the rightful owners can spend Bitcoins.
How To Keep Your Private Keys Safe?
By now, it would have been clear that ‘Private Keys Of Bitcoin Wallets’ are the most important and are not just random numbers.
But if we speak strictly, there are no Bitcoins at all, these are simply numeric entries on a ledger that prove ownership of the coins.
And holding the right private keys gives you the privilege to add or subtract these entries on a specific address of the Bitcoin ledger or transfer these numeric entries to another address within Bitcoin’s blockchain.
You are thus able to make Bitcoin ‘transactions’ on Bitcoin software.
That’s why safeguarding your private keys is of paramount importance, and placing them in cold storage is a very effective way of doing this.
This can be easily done by using a good wallet and by following necessary security practices. And that’s what we are going to discuss in this next section.
#1. Hardware Wallets
A hardware wallet is a device that stores your own private key and public key. And let me tell you some very good hardware wallets are available in the market.
For example, Ledger Nano X & Ledger Nano S.
You will need to keep the seed phrase, which is generated when you first set up your HD wallets, safe, as this is the only way you will be able to access your coins if you forget your password.
#2. Mobile Wallets
A wallet software on a mobile-based client is called a mobile wallet, and these HD wallets are somewhat secure in handling your private keys.
But remember:
Don’t store a large sum of funds on mobile wallets, as it is only as safe as the security of the mobile wallet software itself. Instead, use hardware wallets for storing large amounts of Bitcoins as they are safest when stored offline.
Storing your coins in a device that is not connected to the internet is also referred to as cold storage.
#3. Desktop Wallets
Wallet software clients that can be installed on Windows, Mac, or Linux operating systems are called desktop wallets, and they are generally considered less secure than mobile wallets.
But if you use them with proper encryption and firewall settings, these wallets should be good for storing a significant amount of Bitcoins.
#4. Web Wallet
Web wallets are those wallets that exist purely on the internet and are accessible only through an internet connection and a browser. They are also sometimes referred to as an online wallet.
It is not recommended to store Bitcoins here because you can easily be scammed by a phishing attack or a malware attack.
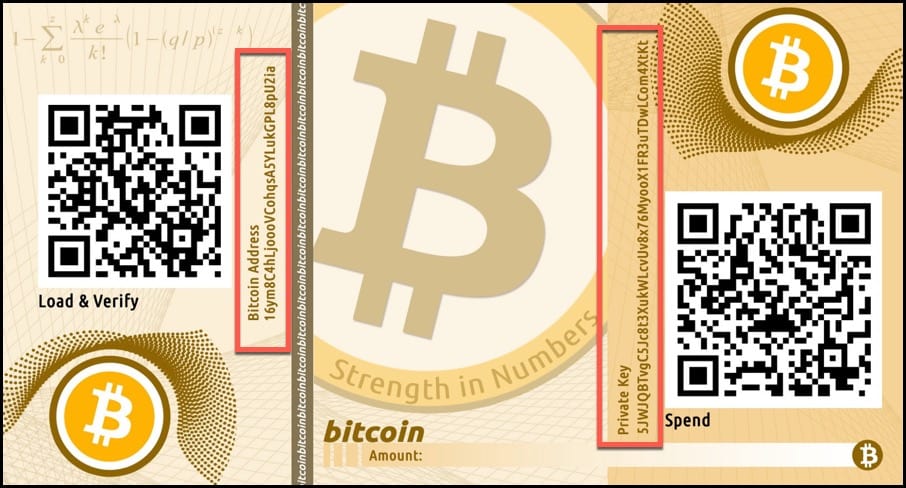
#5. Paper Wallets
Paper wallets are simply a piece of paper with Bitcoin private and uncompressed public keys printed on it.
If you know how to use a paper wallet properly, you may go ahead and store your Bitcoins here, but if you’re not sure, use the above hardware wallet just to be on the safe side.
#6. Brain Wallets
First thing first…
A Brain wallet for storing Bitcoins is a bad idea because the human brain is highly predictable and usually thinks of simple numbers/patterns to generate private keys.
And this nature can be highly predictable as well as lethal.
For example, see this public key:
This key is generated from digit ‘1’ as the brain wallet private key, and if you see it on the blockchain explorer, you will find that 1000s of transactions have happened on this address and a total of approx 7 BTC existed on this address.
There is no mini private key or a compressed key when it comes to a brain wallet. You just have to come up with a number that you will use as a seed to generate your uncompressed key that will be public.
So if you chose this address to store your Bitcoins, it is 100% sure that your coins will have been stolen because ‘1’ as the private key is too predictable.
What Is a Private Key Used For?
Private keys are used for unlocking your Bitcoins locked on a public wallet address only.
Having a mini private key for a particular public Bitcoin address, on which unspent coins are present, is like having the right of ownership and the right to spend them.
This is a marvel of public-key cryptography, one of the main four ingredients which makes Bitcoin possible!!
Does Each Bitcoin Have A Private Key?
Yes & No.
Each Bitcoin can be split up into 10^8 parts, and the smallest unit is a satoshi or a Sat.
So it would be correct to say for each satoshi, or a collection of satoshis which are present on a public address, will have a corresponding private key.
What are some tips to safeguard your BTC private key?
Some actionable security practices to safeguard your private keys…
- Private key encryption is one smart way of safeguarding your keys if you are using a mobile or desktop wallet. But do remember that this encryption password needs to be hard to guess or brute force.
- Use the right firewall settings, malware and antivirus protection softwares.
- Use passphrase and salt both in your private keys or seed. (this is a bit complex, but if you understand it, please do it…)
- If you are using a paper wallet, keep your BTC paper wallet in fireproof, waterproof and ink-proof environments to safeguard your private keys.
- Be aware of phishing attacks trying to fetch your private keys from your web or mobile wallet.
- Store the keys in a wallet import format far away from where you are storing your other valuables.
And if you do these things and use the recommended types of wallets, you will be OKAY.
So that’s all I wanted to share in this article. So now, if you have any questions or suggestions regarding it then feel free to express them in the comments section below.
And if you think this article was helpful to you or can help some of your friends be cautious, then do share it with them.
- Bitcoin Transaction Accelerator: 5 Services to Unstuck Your BTC - September 23, 2023
- What Is Bitcoin Private Key? Everything You Need To Know !! - June 2, 2023
- Best Cardano (ADA) Wallets To Use In 2024 - May 7, 2023
Contents





I have a Multibit backup text file with about 344 characters in it. Is there any way to extract my private key from this? If not why would the backup be in saved this way.
Thank you
Hey @Remi, Welcome to the MoneyMongers
As far as I know, multibit is a very old wallet and they have this way of storing keys in a back-up file. It is defunct too now. But in any case, if you have the back-up you should be able to extract your private keys in a more well-known format.
Is your wallet functional? or have you tried importing your back-up file in the latest version of multibit? Need some more information to help you out !!
Great article very easy to understand! !
Glad to know that Eric