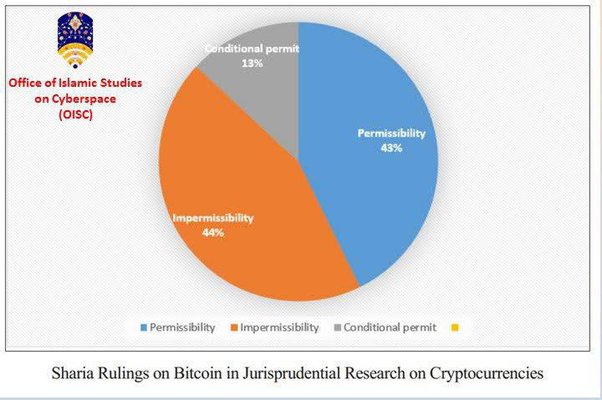
The introduction of Cryptocurrencies sparked a significant debate in Islamic banks and financial institutes.
Is cryptocurrency halal or haram?
Many Muslims worldwide seek clarity on the fatwa regarding cryptocurrency, particularly bitcoin’s halal status, as they contemplate its use.
In this comprehensive concept, we aim to shed light on whether cryptocurrency is considered halal or haram.
Cryptocurrency and other digital forms of money fulfill the essential monetary functions as a medium of exchange, a unit of account, and a store of value.
What Makes Something Halal Or Haram? – An Islamic View
Halal refers to actions, behaviors, and practices that align with Islamic teachings as permissible and lawful.
Specifically in finance, halal transactions follow Sharia principles and involve ethical, transparent practices that benefit society.
In Islam, the term “haram” describes actions or practices that are strictly forbidden.
In the realm of finance, haram refers to transactions involving interest (usury), gambling, speculation, and unethical practices.
These activities contradict Islamic values and principles of economic justice.
Recommended Read: Is cryptocurrency legal in USA?
Halal Finance – Key Principles
- Interest-Free: Avoids unreasonable profit on the sale of essential goods.
- Asset-Backed: Involves tangible assets supporting transactions.
- Ethical Investments: Excludes harmful industries like alcohol and gambling.
- Risk Sharing: Profits and losses are shared between parties.
- Transparency: Clear, honest disclosure in transactions.
- Avoids Speculation: No uncertain or excessive risk-taking.
- Social Responsibility: Benefits society and avoids exploitation.
- Real Economic Value: Supports tangible, productive activities.
- Islamic Contracts: Adheres to Sharia-compliant contracts.
Main Rules of Islamic Finance
The main principles of Islamic finance are rooted in ethical and moral values.
It strictly prohibits usury (riba) and emphasizes the sharing of risks and the backing of assets and social justice.
These guiding principles govern transactions and investments by Sharia law.
Islamic finance places strong emphasis on avoiding speculative practices (known as gharar) and refraining from investing in unethical activities, such as gambling and alcohol.
Additionally, it promotes partnerships and profit-sharing through the concept of mudarabah.
It also strictly prohibits investments in businesses involving pork, interest-based banking, and non-halal industries.
Here are some primary rules of finance under Islam dilemma:
Prohibition of Interest (Riba): Islamic finance strictly prohibits the earning or paying interest (riba) on financial transactions. Its primary focus is on maintaining fairness and discouraging exploitation in wealth exchange.
Risk Sharing (Mudarabah): Partnerships that operate based on profit and loss sharing have the potential to foster ethical investment, as they encourage both parties to share risks and rewards. This approach discourages speculative behavior.
Asset-Backed Transactions (Tawarruq): To ensure validity, transactions should be backed by tangible assets. This promotes genuine value exchange and discourages speculative trading in purely financial instruments.
Prohibition of Uncertainty (Gharar): Contracts should steer clear of excessive ambiguity and uncertainty. They ought to promote transparency and integrity in agreements, thereby reducing the risks of exploitation and fraud.
Ethical Investment (Halal and Haram): Investments in businesses that adhere to Islamic principles are encouraged (halal). On the other hand, activities such as gambling or alcohol, which are prohibited (haram), are strictly forbidden.
Social Responsibility (Zakat and Sadaqah): Islamic finance promotes wealth distribution through the payment of obligatory charity (zakat) and voluntary alms (sadaqah), aiming to support those in need.
Contractual Integrity (Aqd): Contracts should be willingly and honorably entered into, with a strong focus on fair dealings, trustworthiness, and fulfilling promises. This is crucial for establishing a just financial system.
No Speculation (Maisir): The prohibition of gambling and speculative behavior aims to discourage unjust enrichment and instead promote investments anchored in actual economic activities.
Prohibition of Unjust Enrichment (Istisna’ and Salam): Pre-selling goods without transferring ownership (istisna’) and making advance payments for future deliveries (salam) are regulated to prevent exploitation and ensure fairness.
No Financing of Harmful Activities: Investments that support industries detrimental to society, such as alcohol, gambling, and unethical businesses, are strictly prohibited. This policy aims to promote ethical and responsible economic activities.
Recommended Read: What is spot trading in crypto?
Concepts of Cryptocurrency and Money in Islam
In Islamic finance, there is an ongoing debate surrounding whether these digital currencies align with Sharia principles.
In consideration are their roles as a medium of exchange, store of value, and unit of account.
Islamic finance is based on ethical principles such as fairness, transparency, and societal benefit.
In this context, we explore the compatibility of cryptocurrency with these core values, explicitly examining its capacity for risk sharing and avoidance of interest-based transactions.
Views of Islamic Scholars About Cryptocurrency
Islamic scholars hold contrasting views regarding the permissibility of utilizing cryptocurrencies in Islamic finance.
Some assert that investing in cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin, are impermissible due to their lack of tangible assets and speculative value.
Conversely, others contend that as long as cryptocurrencies are used for legitimate and lawful purposes, they can be deemed permissible within Islamic finance as a form of currency.
Furthermore, certain scholars propose the adoption of Islamic-compliant cryptocurrencies that adhere to the principles of Islamic finance while maintaining backing from tangible assets.
Some Islamic scholars’ opinions on cryptocurrencies are mentioned below:
Sheikh Haitham al-Haddad – British Muslim Scholar and TV Presenter
“Islam has no problem with currency per se, but it does have issues with speculative and manipulative practices. Cryptocurrency, by its nature, is highly speculative and highly manipulative, which is why it is haram (forbidden).”
Dr. Mohamad Akram Laldin – Executive Director of ISRA and Professor at INCEIF
“The current cryptocurrencies, or at least the vast majority of them, are not based on any tangible assets and therefore are not acceptable in Islamic finance.”
Mufti Muhammad Abu Bakar – Sharia Adviser and Compliance Officer at Blossom Finance
“It is permissible to deal in these currencies if the exchange is made hand to hand and the deal is settled on the spot.”
Sheikh Dr. Muhammad Taqi Usmani – Retired Judge, Vice President of Jamia Darul Uloom
“Bitcoin is not permissible in Islamic finance because it is not a currency in the traditional sense and is not backed by tangible assets.”
Is Cryptocurrency Halal or Haram?
Sharia scholars worldwide hold differing opinions on whether Bitcoin is halal or haram.
Those who deem it haram primarily argue that the speculative nature, illicit activities associated with Bitcoin markets, and its lack of centralized authority make it unacceptable.
Conversely, scholars who consider Bitcoin to be halal assess its decentralization, transparency in transactions, and compatibility with Islamic contract rules that emphasize effective storage and possession (known as “mal”).
In practice, whether Bitcoin is considered halal or haram depends on individual evaluations and the jurisdiction one resides.
Notably, countries like Egypt and Turkey lean towards a haram stance while Malaysia and Bahrain interpret it as halal based on scholarly interpretations mentioned earlier.
Interestingly, even major Muslim nations like the UAE and Saudi Arabia are exploring the creation of their digital currencies in support of digital assets.
This underscores a positive perspective within these regions regarding cryptocurrencies in general.
Recommended Read: What are the types of crypto exchanges?
Why Is Cryptocurrency Considered Haram?
There are several concerns surrounding the perceived prohibition of cryptocurrency in Islam.
First, its decentralized nature gives rise to uncertainty regarding regulatory compliance and alignment with monetary policy.
Additionally, the excessive volatility and speculative trading go against the principles of stability and fair exchange.
These factors contribute to a skeptical view on whether cryptocurrency is compatible with Islamic finance principles.
Below are 10 Reasons why cryptocurrency is considered haram:
- Gharar (Uncertainty): Unpredictable value undermines fair exchange.
- Riba (Interest): Earning through price appreciation may be considered usury.
- Speculation: Risky trading conflicts with Islam’s aversion to gambling.
- Lack of Tangibility: Digital nature clashes with asset-backed financial systems.
- Anonymity: Concealed ownership raises concerns about transparency and accountability.
- Market Manipulation: Vulnerability to manipulation contradicts just market principles.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Lack of oversight conflicts with Islamic financial ethics.
- Community Welfare: Cryptocurrencies may not contribute to social and economic welfare.
- Misuse: Potential for illicit activities clashes with Islamic values.
- Ethical Concerns: Environmental impact and energy usage pose moral dilemmas.
Cryptocurrency Halal Investment Guide
Cryptocurrency can be confusing for anyone, and it becomes even more challenging for Muslims due to the complex nature of investment and finance rules.
As a Muslim investor, it’s crucial to follow specific tips to ensure the halal usage of cryptocurrency.
- Use a Halal Cryptocurrency and Broker: As stated in Islam financial laws, you must ensure the broker you use follows Islamic law. You can invest in halal digital currencies if you do your due diligence.
- Do not trade Futures: You can’t analyze and predict the future price of a digital coin with Futures in cryptocurrency. In Islamic culture, this is considered gambling and haram. So futures trading is considered haram.
- Do not stake cryptocurrency: You stake cryptocurrency by storing it in a digital wallet and earning interest. It’s like a savings account, but it’s considered haram in Islam.
- Pay your Taxes and follow the rules: You should pay taxes on cryptocurrency income if your country requires it.
Final Words
Is cryptocurrency considered halal?
The question sparks a debate among various groups.
However, it appears that cryptocurrency can be deemed halal as long as it is not utilized for illicit activities and investors refrain from speculative intent for profit.
Ultimately, the decision to invest in cryptocurrencies rests with each individual.
Some may feel at ease with the idea of investing, while others prefer to await further clarification on Islamic rulings concerning crypto.
What are your thoughts?
Do you believe cryptocurrency aligns with halal principles, or do you consider it haram?
Share your opinions below in the comments section. Additionally, you may also want to know if crypto leverage trading is halal or haram.