Think of cryptocurrency exchanges as bustling digital marketplaces, much like traditional stock exchanges. But instead of stocks, they deal in cryptocurrencies.
But the actual knowledge is understanding how they function, what services they provide, and why they are crucial in digital currencies.
Stick around as I dive into what a crypto exchange is, and unravel how they work.
Whether you’re a newbie or just looking to brush up on the basics, this guide is for you!
What is a Crypto Exchange?
A cryptocurrency exchange facilitates the buying, selling, and trading of cryptocurrencies.
These digital marketplaces operate in a way that’s similar to traditional stock exchanges but with some key differences.
Users can buy and sell crypto like BTC, ETH, or Litecoin. These transactions can be done with fiat currencies or other cryptocurrencies.
Crypto exchanges offer trading pairs, allowing users to exchange one cryptocurrency for another.
For example, a trading pair might be BTC/ETH, meaning you can trade Bitcoin for Ethereum and vice versa.
By bringing together many buyers and sellers, crypto exchanges provide liquidity to the market. This ensures enough volume for users to buy or sell without significantly affecting the price.
Many crypto exchanges offer staking, lending, and derivatives trading services.
Exchanges typically charge fees for trading, depositing, or withdrawing funds. These fees vary on the platform and the type of transaction.
How Do Crypto Exchanges Work?
Crypto exchanges operate as digital marketplaces where traders can buy, sell, or exchange crypto for digital or traditional fiat currencies like US dollars or Euros.
The basic principle behind their operation is quite simple – they allow users to trade crypto based on the current market price.
Now, let’s break down what exchanges themselves bring to the table.
Market Making: When there is more interest from the market to trade a currency, the trading volume on the exchange increases. This, in turn means lower volatility and price fluctuation. This makes it more difficult to manipulate the price of a listed asset.
Volatility is essential for most coins as it is a majorly volatile asset. So if, in the time required to complete the transaction, the price of the token changes, then the trader does not receive the return they were expecting.
This further damages the reputation of the asset class
So, higher trading volumes ensure faster transaction processing, thereby avoiding the impact of fluctuations.
Coin Listings: An exchange brings trading volume to every cryptocurrency it lists on the platform.
Any new coin not on a centralized exchange experiences massive slippage, and order books are very shallow.
Once they are listed on an exchange like Binance, it brings attention and, consequently, more traders who want to buy and sell them.
Order Matching: Centralized exchanges receive orders from individual users or institutional clients for transactions.
What the exchanges then do to match them is to match the buy and sell orders that are at the same price.
As explained above, exchanges are also market makers that provide liquidity to tokens and make the transactions go through faster.
Storing and withdrawing: The exchange can typically send cryptocurrency to a user’s cryptocurrency wallet if they wish to withdraw it.
It is a simple case of inputting your external wallet address and paying the network fee.
Some exchanges have the option to withdraw your tokens into prepaid cards that help preserve anonymity. These cards can then be used to withdraw funds from any ATM worldwide.
Decentralized exchanges: Exchanges such as Etherdelta, IDEX, and HADAX do not store users’ funds on the exchange but facilitate peer-to-peer cryptocurrency trading.
Decentralized crypto exchanges resist security problems that affect other exchanges but suffer from low trading volumes.
Maker & Taker Model: Most major centralized exchanges employ a maker and taker model. A market maker places orders that get added to the order book and may not be matched instantly. An example of this is limit orders.
On the other hand, a market taker takes liquidity away from the market. They do this by placing orders that will be filled immediately using the order book, for example, market orders.
Both these entities play an important role in creating the market and ensuring it reaches a fair value.
Order Books: The exchange matches buy and sell orders in its order book.
When a buy and sell order matches, the exchange platform executes the trade, and the corresponding cryptocurrencies change hands.
Order books record the prices the trades are placed at, which are available for any user to look at and analyze.
Depending on whether you are a beginner or an advanced trader, you can view the order book in different ways and glean different information from it.
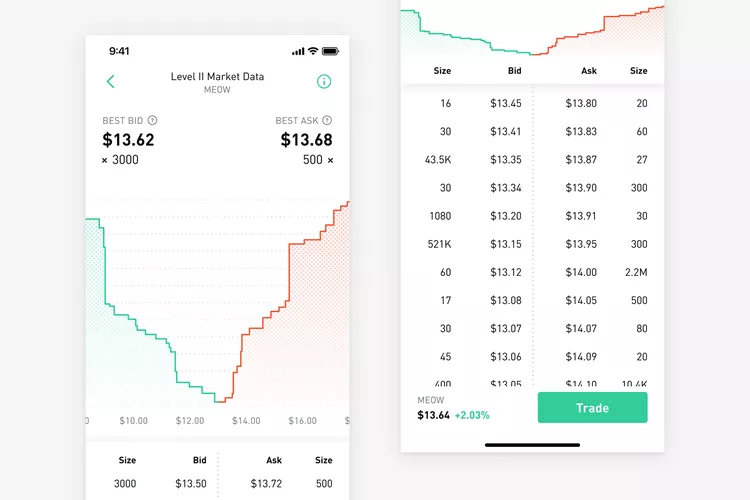
Below is the regular way that most order books look like. This one is from RobinHood. The Size column tells you the number of coins being traded, and the Bid column shows you the price at which the order will be filled.
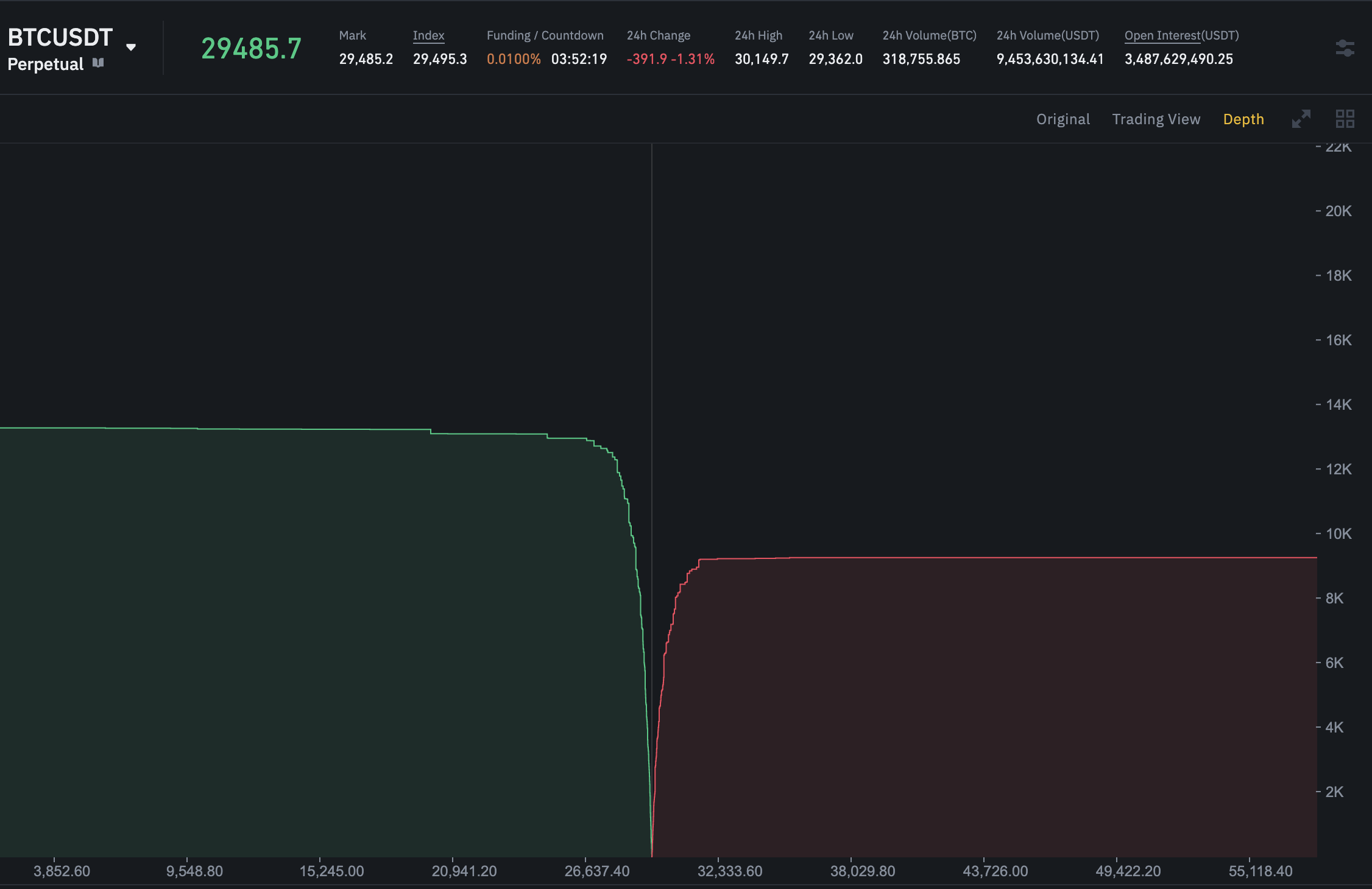
Another way to view an order book is shown below as a screengrab from Binance Futures. This is more of a visual representation of the order book shown above.
This way of looking at it gives you more intuitive information quickly. Some experienced traders prefer this to a regular order book view.
It’s important to note that while all exchanges function on these basic principles, there can be significant differences in their specific features, security measures, regulatory compliance, etc.
Therefore, choosing an exchange that aligns best with your trading goals and risk tolerance is crucial.
Choosing the Right Exchange
Choosing the right crypto exchange is a critical decision that greatly affects your trading experience.
If you’ve ever wondered, “Which exchange should I choose?” you’re not alone.
You must consider many things, like fees, the platform’s security measures, and the available coins.
Your favourite exchange should have a high trading volume and liquidity to buy your coins at a fair price.
This is a conversation for another day that you will also need to take seriously.
Security Considerations
When you select your platform, you should check what features they have to protect your account and your coins.
Some things that come to mind are two-factor authentication, encryption, and regular security audits.
Platforms like Binance and KuCoin have a history of being hacked, so you might want to remember that when you choose.
Not that it will happen again, but knowing that the platform has taken measures to rectify its shortcomings will put you at ease.
Read a few user reviews on websites like TrustPilot before you deposit any money there.
Regulatory Aspects
Reputable exchanges often comply with legal regulations set by governmental bodies.
These regulations might include Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements aimed at preventing illegal activities.
Compliance with these regulations signifies an exchange’s commitment to operating within legal boundaries.
Fees and Costs
Understanding the fee structure can save you a surprising amount of money in the long run.
Almost every exchange charges a fee for executing a trade. This could be a fixed amount or a percentage of the trade value.
Some exchanges even offer tiered fee structures based on your trading volume.
Are you planning to deposit or withdraw funds?
Be aware that these actions might carry associated fees.
Some exchanges charge for deposits and withdrawals using bank transfers or credit cards.
So, compare these costs across various platforms to find the most favourable terms.
Pros and Cons of Using Exchanges
Ready to explore both the good and the not-so-good aspects of using exchanges?
Let’s break it down:
Pros:
- Accessibility: Exchanges make it simple and accessible for both beginners and experts. They often provide user-friendly interfaces and tools to guide you through buying and selling.
- Liquidity: Ever wondered how quickly you can convert your crypto into cash? Exchanges generally offer high liquidity, meaning you can buy or sell large volumes without significantly impacting the market price.
- Security Measures: Many exchanges implement robust security protocols, like two-factor authentication and cold storage. Your investments are typically safer than they would be in a personal wallet.
Cons:
- Fees: Trading isn’t free. You might encounter transaction fees, withdrawal fees, or other costs.
- Regulatory Risks: Regulations can vary widely between countries and regions. Some exchanges might not comply with local laws, leading to potential legal issues.
- Limited Control: When you store your crypto on an exchange, you may not completely own your private keys.
- Potential Downtimes: Exchanges can experience downtimes due to maintenance or high traffic, which might impact your ability to trade when you want to.
- Customer Support Issues: Some exchanges might have limited or slow customer support, which can be frustrating when encountering problems.
Alternative Methods to Exchanges
So, you’ve grasped what crypto exchanges are and how they function, but did you know there are alternatives to trading on exchanges?
Explore other options that suit your trading style or security preferences.
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Trading: P2P trading allows individuals to transact crypto directly with each other. Platforms like LocalBitcoins facilitate these trades, often providing an escrow service to enhance security.
- Over-the-Counter (OTC) Trading: This method involves buying or selling cryptocurrencies directly with a counterparty, often facilitated by OTC desks. It helps in avoiding price slippage on exchanges.
- Crypto ATMs: Believe it or not, there are ATMs where you can withdraw or deposit cryptocurrencies. These machines are located in various cities around the world. A tangible touch to the digital world, how novel is that?
- Using a Personal Wallet for Direct Transactions: You can also conduct direct transactions from personal crypto wallets to those of others. You can use this method to pay for goods and services or transfer funds to friends and family.
Conclusion
Navigating the world of crypto exchanges can seem daunting.
But now, with an understanding of crypto exchanges, how they work, and the considerations involved, you’re well-equipped to dive into the crypto trading arena.
So, what’s next?
Explore, research, and choose the platform or method for your goals and risk tolerance.
Exciting opportunities await in the crypto world.
Happy trading!